Sikkim
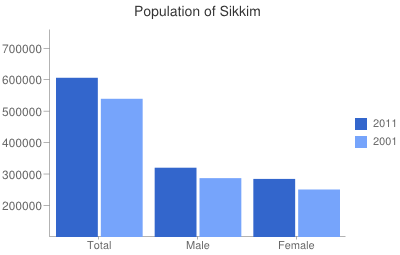
The Sikkim census of 2011 says population of Sikkim is the least in all of India. This thinly populated state has a population of mere 6.10 lacs, and has grown by approximately one lac since the last census.
The state of Sikkim is also the second smallest state in India, and thus, the population density here isn't as low as you'd expect it to be. The density is less than 100 in Sikkim, and has undergone significant increment. The population growth rate is another factor indicating the population status. In Sikkim, the decadal growth rate of population has considerably reduced to just above 12%. Percentage of literates however, has increased by about 15%, which is a huge leap toward progress. Increase in female literacy also tells an optimistic story.
The gender ratio in Sikkim has increased from 875 in 2001 to 890 females for every 1000 males in 2011 census. As with most north eastern states in India, the land has not been developed largely. Hence, only over 20% of the population of Sikkim lives in cities. The capital city Gangtok is also the largest one in Sikkim. While, urban population is growing at an alarming rate of above 150%, the rural population isn't growing at all, but is decreasing.
The languages spoken in the Sikkim state includes Nepali, Bhutia, Lepcha, Limbu, Newari, Kulung, Gurung, Manggar, Sherpa, Tamang and Sunwar. In total Sikkim (SK) state comprises 4 districts. The ISOCODE assigned by International Organization for Standardization for Sikkim state is SK.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Percantage of total Population
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Child Population (0-6 Age)
|
|
|
Male Population (0-6 Age)
|
|
|
Female Population (0-6 Age)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Source: Census of India 2011